Setting up GraphQL with Spring boot
09 Jun 2022
Before you read further, I’d love to welcome you again to Serendipity by Design. If you think the title of this blog sounds weird, then you’re not alone.
Futhermore, I know It’s been months since I last made an update here, won’t happen anymore, I really hope that this turns out to be a weekly issue where you get updates. I’ll do all that’s within my power, salut!😎😉
PS: I have some exciting topics saved on my drafts, so yeah I’ve been cooking…
Let’s talk about spring boot and the latest official release for graphQL 1.0. For the non-tech folks, no vex. But I’d try my best to explain this in layman's terms, so let’s go…
GraphQL release became official following the recent release of springboot 2.7.0 see image attached below.

A brief introduction to what graphQL is, and what I think you should know to get started.
GRAPHQL 101
GraphQL is a web query language that is used to build web APIs Application Programming Interface. The most common way to do this was with REST API(Representational State Transfer), but the increase in demand for more data in building a web application meant an increase for more endpoints to feed to the user, from third-party services, IoT devices, microservice, and mobile applications all requiring a specific kind of data. No matter the complexity of these applications, they were often limitations. The data sets needed on different applications are usually not the same, some required priority on faster connections, others required robust data to process information in real time, they were so many restraints to be concerned about.
Then came the official release of GraphQL to the public by Facebook now META in 2015. It was introduced to at least solve this issue. You can execute a specific query command through your endpoints to get the specific kind of data needed for your applications. These meant that services could fetch just the right amount of data, from a single query.
GraphQL Type System
Okay, we’re now one step closer to building our application. Having an understanding about the graphql type system will help you in building your graphql schema, which is responsible for communicating with client requests when a query is executed.
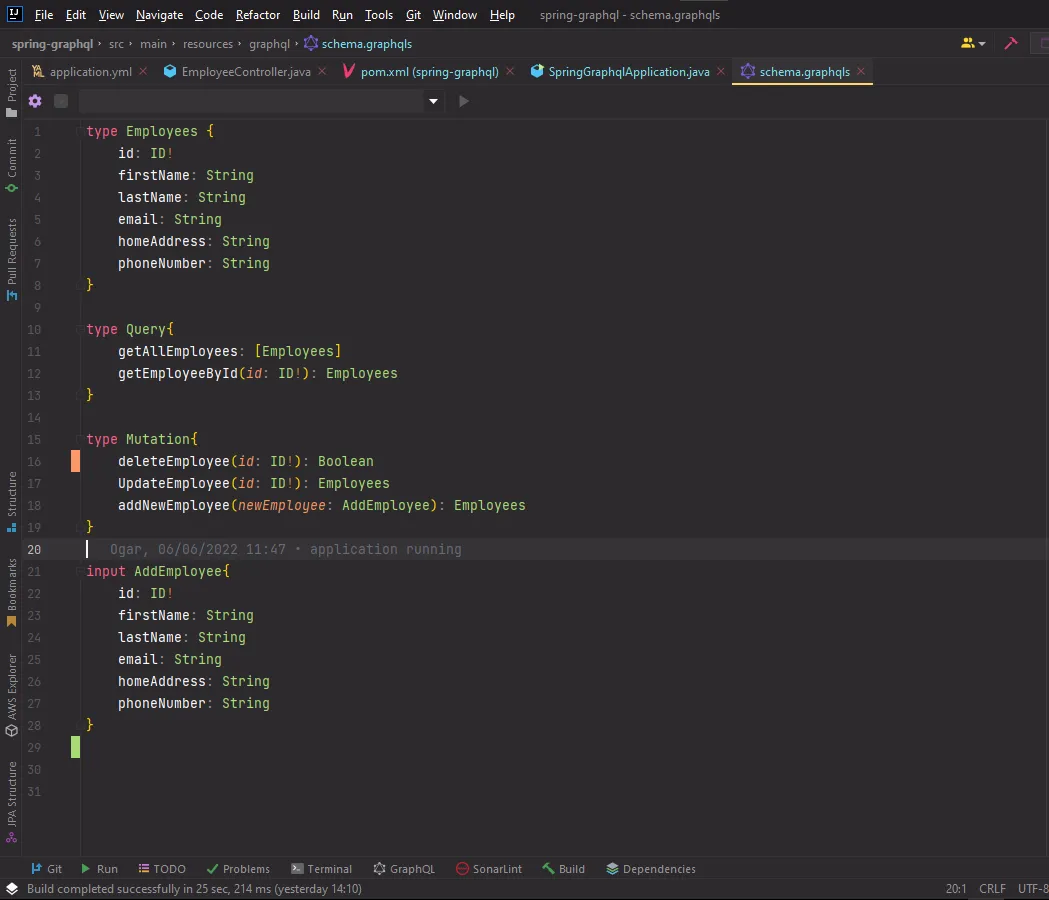
An example look at the schema created for an employee web API.
The employee type has an ID, firstName, lastName, email, homeAddress, and phoneNumber. In this case through a single query, data can be fetched to get all employees by firstName, or even email.
The graphql schema is basically the same that is written across multiple programming languages, similar to JSON(Javascript Object Notation). You can read the schema structure in a Java application in the same way, for a Javascript, Go or C++ application.
In setting up your application, you can decide what object types and fields you want present in your application. Your object “type“ is synonymous to the model that is created for your application. In the image above, I created a model that contains Employees (id, firstName, lastName, email, homeAddress, and phoneNumber). The values on the right defines the parameters that should be inputed (string, boolean, int: recall data types), while the values on the left represents the data field names. ! attached to a value type indicates that it should not return a null response upon query.
Operation Types
Query: Used to read data. Practically performs the same function similar to the GET method in a REST API. In spring boot you use the annotation @QueryMapping.
Mutation: Used to perform Delete, Update and Create data similar to PUT, POST and DELETE methods in REST API. In spring boot you use the annotation @MutationMapping.
Subscription: Likely performs the same function as the Query method to get data, but in this case is used for operations that their results tends to change over time given for a certain period.
Building our Server
Now let’s take a look on how to build our web server. For the sake of this demo purpose I’ll try to not make this a boring and long read, I’ll just add snipets of my code samples which I think are important and helpful. I already did a ton of explanation which should get your started and I will assume you are already familiar with Java and Spring boot or building web APIs.
If you aren’t, worry not. I’ll share some of the best materials I’ve come across on the web at the later ending of this post. If you need to see my working code, make a request and I’ll drop a link to the github repo.
Dependencies you need to get started, here’s what my pom.xml looks like.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-graphql</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.graphql-java</groupId>
<artifactId>graphiql-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webflux</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.graphql</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-graphql-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.24</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
PS: You’ll need to add the spring graphiql dependency. The graphiql dependency is a UI companion for your graphql server to perform query operations and test your APIs on your browser, no need for a HTTP client.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.graphql-java</groupId>
<artifactId>graphiql-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2</version>
</dependency>
In your application.yml also lookout for the spring-graphql-graphiql-enabled = true to enable the graphiql browser UI.
spring:
graphql:
graphiql:
enabled: true
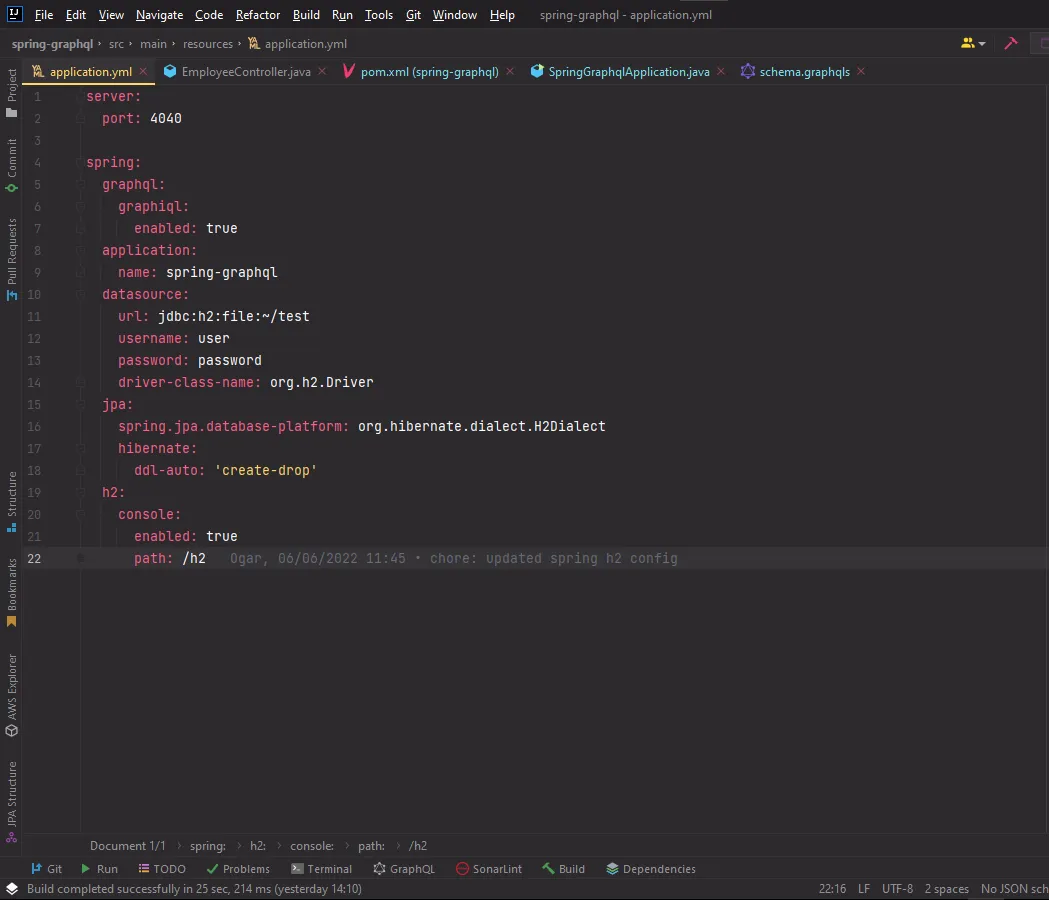
I used the H2 database and spring data jpa just for this demo application. In a real world project, you can choose to use an SQL or No-SQL database.
My application.yml file.
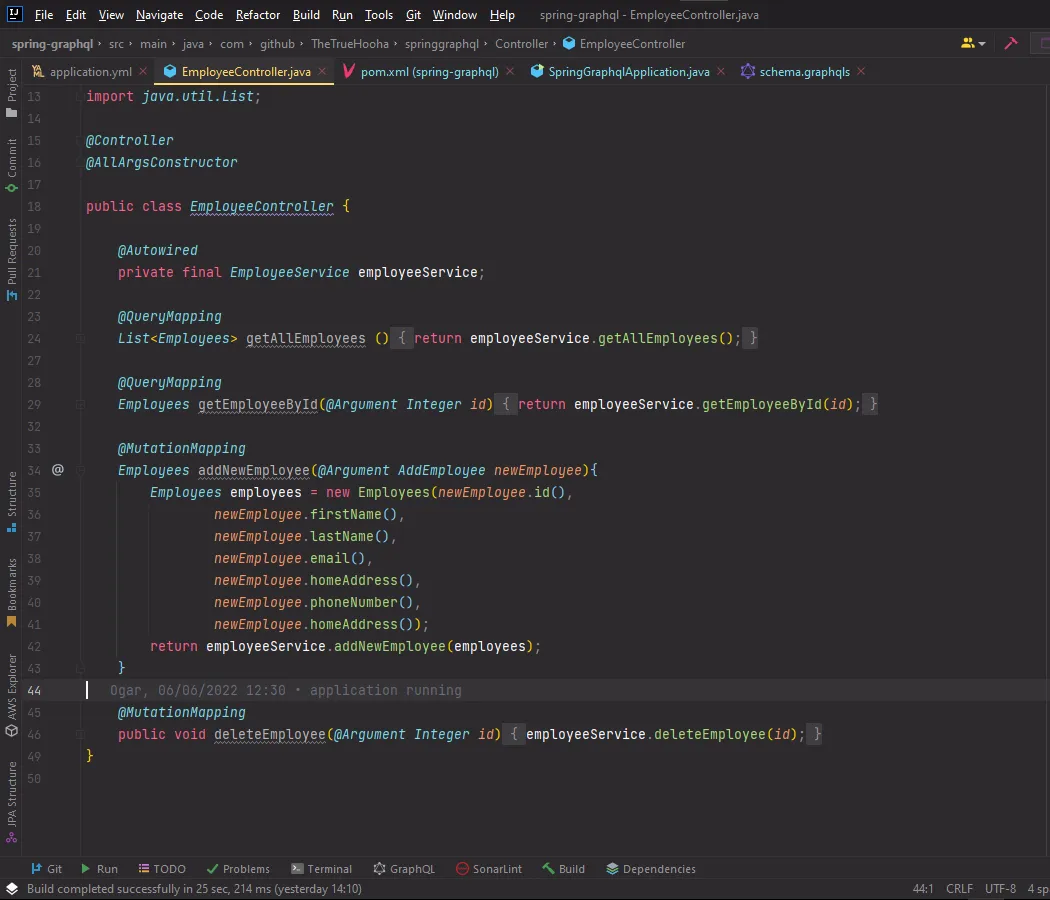
My controller class
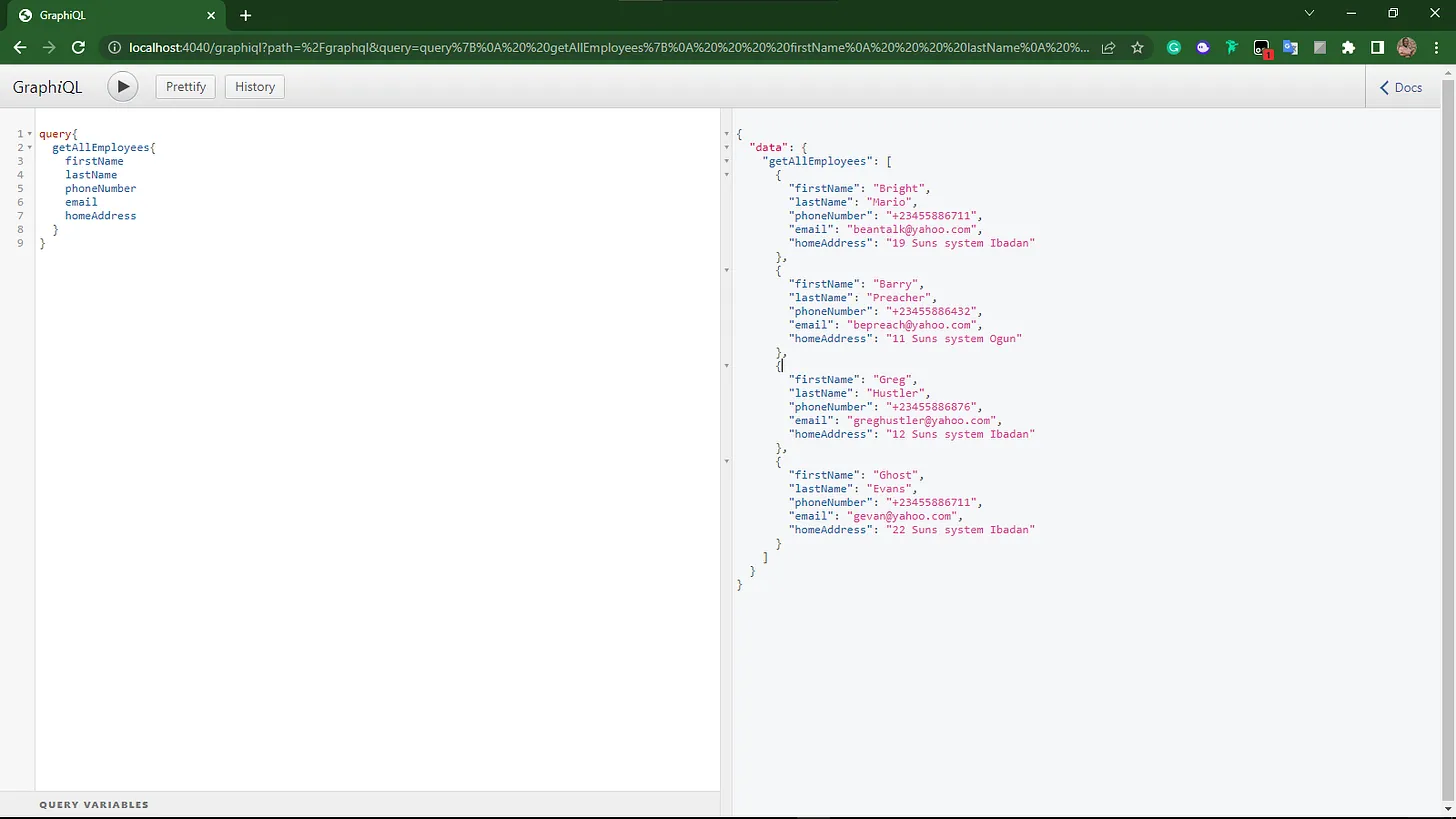
Graphql query results
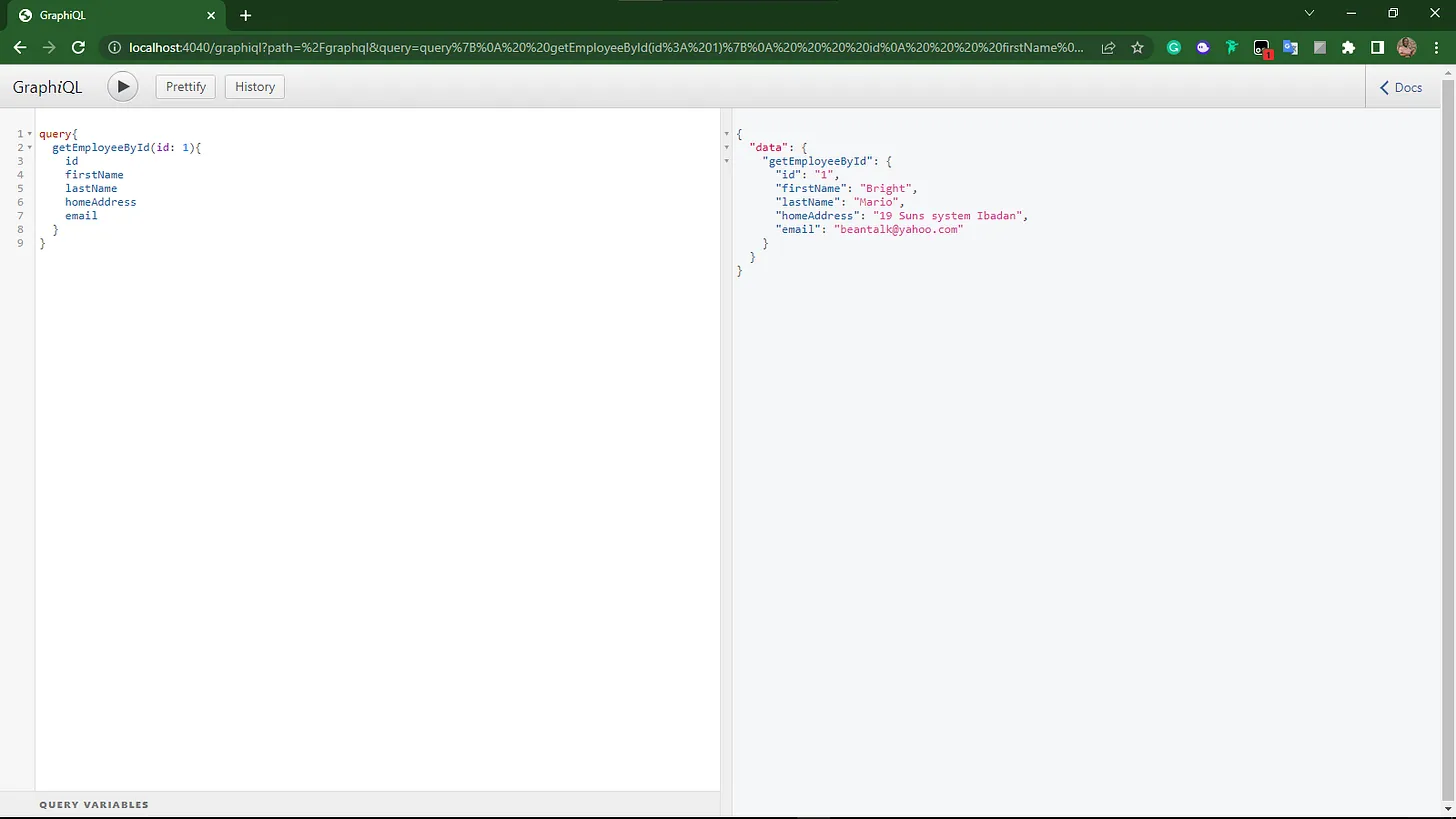
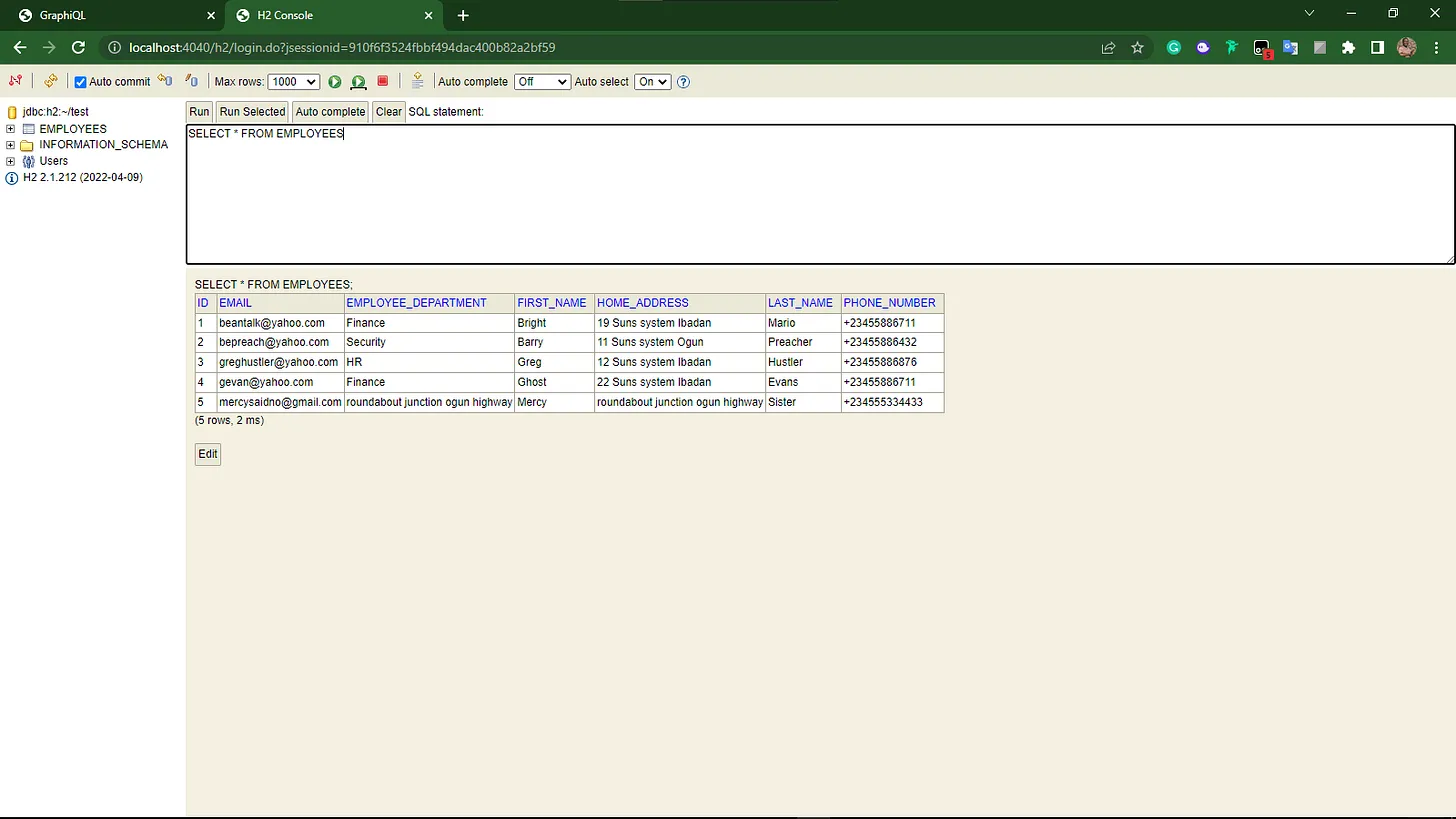
TL;DR
Important Resources
- Graphql Resources
- Getting started with graphql
- Spring Rest Services
- Java Roadmap
- Use the roadmap as a guide on how to start, find free courses online.
PS: Anticipate an issue about structured list plus resources to learn java, and how I started my java journey.
Thank you for reading, and till next time….
Don’t forget to like and comment!
Aloha ❤
David.